The key industries that rely on offshore containers include oil and gas, marine, and renewable energy. In the oil and gas sector, offshore containers are used to transport drilling equipment, spare parts, and hazardous materials. In the marine industry, they serve as storage units for tools and supplies needed for ship maintenance and repair. In the renewable energy sector, particularly offshore wind farms, these containers are used to store and transport components such as turbine blades and nacelles.
Compliance and safety are paramount in the design and use of offshore containers. These containers must adhere to stringent international standards and certifications to ensure they can withstand the extreme conditions of offshore environments. Compliance with these standards not only ensures the safety of personnel and equipment but also minimizes the risk of environmental damage.
Types of Offshore Containers
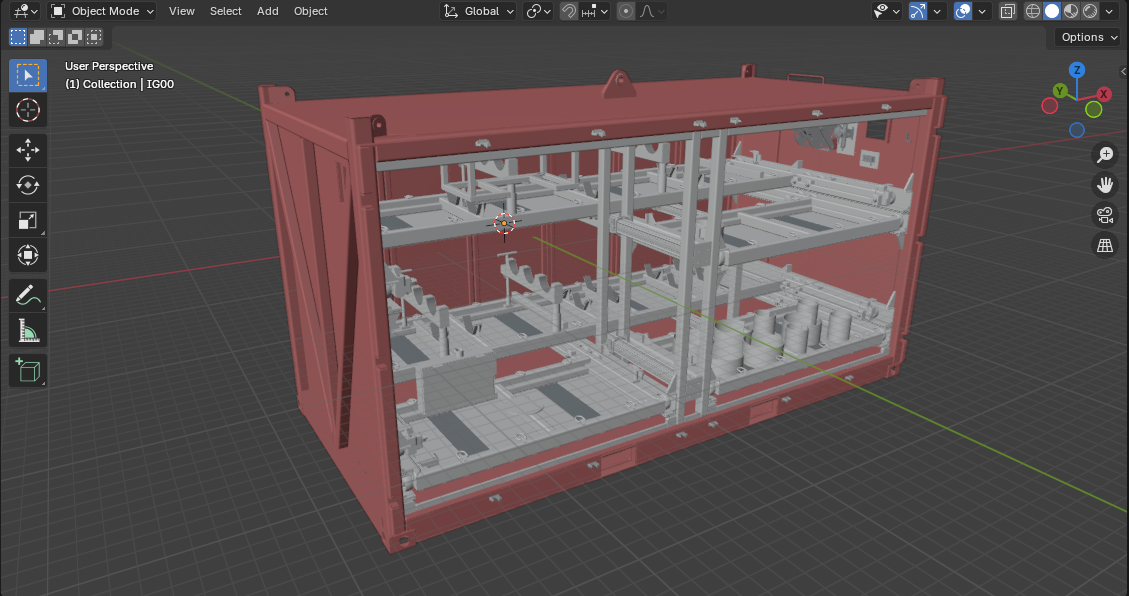
Cargo Carrying Units (CCUs) are the most common type of offshore containers. These units are designed to transport general cargo, such as tools, equipment, and supplies. Standard cargo containers are typically 20 or 40 feet in length, while half-height containers are used for smaller loads or when space is limited. CCUs are essential for the efficient movement of materials between onshore bases and offshore installations.
Offshore reefer containers are specialized units designed to transport temperature-sensitive goods, such as food, medicine, and chemicals. These containers are equipped with refrigeration systems that maintain a consistent temperature, ensuring the integrity of the cargo. Offshore reefer containers are critical for supporting the health and safety of offshore workers, as well as for the safe transport of hazardous materials.
Offshore accommodation containers provide living quarters for offshore workers. These units are equipped with essential amenities, such as beds, kitchens, and bathrooms, to ensure the comfort and well-being of personnel. Accommodation containers are often used in remote locations where permanent housing is not available, making them a vital component of offshore operations.
Hazardous material offshore containers are designed to transport dangerous goods safely. These containers are constructed with reinforced walls and specialized ventilation systems to prevent leaks and explosions. They are essential for the safe transport of chemicals, fuels, and other hazardous materials in offshore environments.
Custom offshore containers are tailored to meet specific operational needs. These units can be designed with modular components, allowing for easy reconfiguration and adaptation to different functions. Custom containers are often used for specialized applications, such as workshops, laboratories, or storage for sensitive equipment.
Offshore Container Certification and Standards
Certification is a critical aspect of offshore container design and construction. The most widely recognized standards for offshore containers are DNV 2.7-1, 2.7-2, and 2.7-3, which set out the requirements for the design, construction, and testing of offshore containers. These standards ensure that containers can withstand the extreme conditions of offshore environments and provide a safe and reliable solution for transporting goods.
ISO 10855 is another important standard for offshore containers. This standard specifies the dimensions, ratings, and structural requirements for offshore containers, ensuring they are compatible with global supply chains. ISO certification is essential for ensuring the interoperability and safety of offshore containers.
Bureau Veritas and Lloyd’s Register are two of the leading certification bodies for offshore containers. These organizations provide independent verification of container design and construction, ensuring compliance with international standards. Certification from these bodies is a mark of quality and reliability, providing assurance to shipowners and operators.
The U.S. Coast Guard and the American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) also set standards for offshore containers. These standards are particularly important for vessels operating in U.S. waters, as they ensure compliance with local regulations. Certification from these bodies is essential for ensuring the safety and legality of offshore containers in U.S. waters.
Certification matters for offshore safety and compliance. It ensures that containers are designed and constructed to withstand the extreme conditions of offshore environments, reducing the risk of accidents and environmental damage. Certified containers provide peace of mind to shipowners and operators, knowing that their equipment meets the highest standards of safety and reliability.
Offshore Container Construction and Design
The construction and design of offshore containers are tailored to meet the unique challenges of offshore environments. These containers are typically constructed using high-quality materials, such as corrosion-resistant steel and aluminum, to ensure durability and longevity. Reinforced structures, including thicker walls and heavy-duty corner castings, provide additional strength and stability.
Weatherproofing and corrosion resistance are critical aspects of offshore container design. These containers are often treated with advanced coatings and surface treatments to protect against saltwater, UV radiation, and mechanical wear. These treatments extend the service life of the containers and ensure reliable performance in harsh conditions.
Lifting and transport features are also essential components of offshore container design. These containers are equipped with pad eyes, slings, and D-rings to facilitate safe and efficient lifting and handling. These features ensure that containers can be easily transported and positioned using standard offshore handling equipment, such as cranes and forklifts.
**Offshore Container Rental vs. Purchase**
The decision to rent or purchase an offshore container depends on the specific needs of the operation. Renting is often the preferred option for short-term projects or when the need for containers is temporary. Rental agreements typically include maintenance and servicing, reducing the burden on the operator. Short-term rental options provide flexibility and cost savings for projects with limited durations.
Purchasing offshore containers is a more suitable option for long-term operations or when the need for containers is ongoing. Ownership provides greater control over the containers and allows for customization to meet specific operational needs. While the initial investment is higher, the long-term benefits of ownership, such as reduced rental costs and increased flexibility, often justify the expense.
Key suppliers for offshore container rentals and sales include companies such as Suretank, Cargostore, and Almar. These suppliers offer a range of containers to meet different operational needs, from standard cargo units to specialized containers for hazardous materials. Choosing a reputable supplier is essential for ensuring the quality and reliability of the containers.