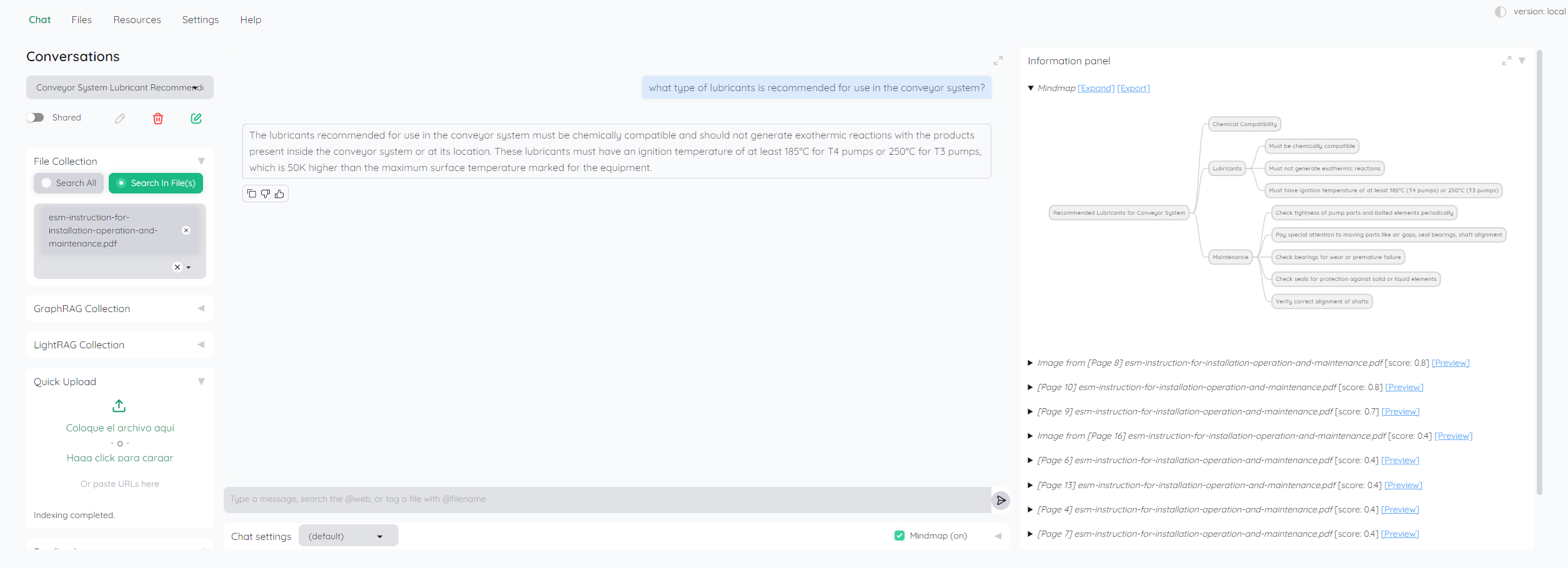
The world of work has undergone a seismic shift in recent years, with remote work and digital transformation emerging as defining trends across industries. For mechanical engineers, this evolution has brought both challenges and opportunities, reshaping how we design, collaborate, and innovate. As organizations adapt to this new reality, a host of technologies are enabling engineers to work more efficiently and effectively, regardless of their physical location.
One of the most significant enablers of remote work is the widespread adoption of cloud-based platforms. These tools allow mechanical engineers to access design software, simulation tools, and project management systems from anywhere in the world. Whether working on a complex CAD model or analyzing finite element analysis (FEA) results, engineers can now collaborate in real-time with colleagues, clients, and suppliers. This level of connectivity ensures that projects stay on track, even when team members are dispersed across different time zones.
Digital twins have also become a cornerstone of remote collaboration. These virtual replicas of physical systems or products allow engineers to monitor, simulate, and optimize designs in a virtual environment. For example, a mechanical engineer working remotely can use a digital twin to test the performance of a new component under various conditions, share insights with the team, and make data-driven decisions without needing to be on-site. This capability not only enhances collaboration but also reduces the need for physical prototypes, saving time and resources.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are playing an increasingly important role in remote work environments. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify trends, predict outcomes, and suggest optimizations. For mechanical engineers, this means being able to leverage AI to refine designs, improve energy efficiency, or predict equipment failures. These insights can be shared seamlessly across remote teams, enabling a more collaborative and data-driven approach to problem-solving.
Communication and collaboration tools have also evolved to meet the needs of remote work. Video conferencing platforms, instant messaging apps, and collaborative whiteboards have become essential for maintaining connectivity and fostering teamwork. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are taking this a step further, allowing engineers to visualize complex designs and interact with them in immersive environments. For instance, a remote team can use AR to overlay a 3D model onto a physical prototype, enabling real-time feedback and adjustments.
Another key trend is the rise of remote monitoring and predictive maintenance technologies. IoT-enabled sensors and devices allow engineers to monitor the performance of machinery and equipment from afar, collecting real-time data on parameters such as temperature, vibration, and pressure. This data can be analyzed using AI algorithms to predict potential failures and schedule maintenance proactively. For mechanical engineers, this means being able to ensure the reliability and efficiency of systems without needing to be physically present.
However, the shift to remote work and digital transformation is not without its challenges. Adapting to new tools and workflows requires a commitment to continuous learning and upskilling. Organizations must invest in training and support to ensure that their teams can fully leverage these technologies. Additionally, the increased reliance on digital tools raises concerns about data security and privacy, which must be addressed through robust cybersecurity measures.
In conclusion, remote work and digital transformation are reshaping the landscape of mechanical engineering. By embracing cloud-based platforms, digital twins, AI, and advanced communication tools, engineers can work more efficiently and collaboratively, regardless of their location. These technologies are not just enhancing productivity—they are enabling engineers to push the boundaries of innovation and deliver solutions that were once unimaginable. As we continue to navigate this digital era, the ability to adapt and thrive in a remote work environment will be a key driver of success for mechanical engineers and the organizations they serve.
